Применение антимоната натрия в качестве замены триоксида сурьмы в огнестойкостях волокна: технические принципы и преимущества и анализ недостатков.
---
Введение
По мере того, как глобальные требования к экологическому дружелюбию и безопасности пламенных материалов увеличиваются, волокна и текстильная промышленность срочно необходимо изучить альтернативы традиционным огнестойчащим. Триоксид антимоны (SB₂O₃), в качестве основного синергиста систем галогенового огнезависимого огня, давно доминирует на рынке. Тем не менее, его потенциальная токсичность, обработка пыли и экологические споры побудили отрасль искать лучшие решения. Благодаря экспортному контролю Китая на сурьме, триоксид сурьмы не хватает на международном рынке, а антимонат натрия (NASBO₃) привлек к себе внимание благодаря его уникальным химическим свойствам и функциям замены. Техническая команда Urbanmines Tech. ООО, в сочетании с фактическим опытом использования и замены антимоната натрия, составила эту статью с технической точки зрения, обсуждается с знающими людьми в отрасли, осуществив возможность замены антимоната натрия, и проанализировала его принципы преимущества и недостатки.
---
I. Сравнение мебельных механизмов: синергетический эффект антимоната натрия и триоксида сурьмы
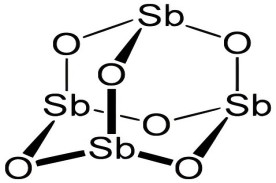
1. Пламя замедляющего механизм традиционного SB2O2
SB2O2 должен работать синергически с галогенными огнестойчанными затихами (такими как соединения брома). Во время процесса сгорания эти два реагируют на образующие летучие галогениды сурьмы (SBX2), которые ингибируют сжигание по следующим путям:
Газовая фазовая огнестойкость: SBX₃ захватывает свободные радикалы (· H, · OH) и прерывает цепную реакцию;
Конденсированная фазовая огнестойкость: способствует образованию углеродного слоя для изоляции кислорода и тепла.
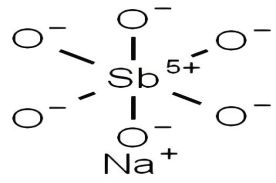
2. Огнестиративные свойства антимоната натрия
Химическая структура антимоната натрия (Na⁺ и Sbo₃⁻) дает ему двойную функцию:
Высокая температурная стабильность: разлагается, чтобы генерировать SB₂O₃ и NA₂O при 300–500 ° C, а высвобождающий SB₂O₃ продолжает сотрудничать с галогенами для задержки пламени;
Эффект щелочной регуляции: Na₂O может нейтрализовать кислые газы (такие как HCl), вырабатываемые сжиганием и снижает коррозовность дыма.
Ключевые технические точки: сурьма натрия высвобождает активные виды сурьмы путем разложения, достигая огнестойкого эффекта, эквивалентного SB2O₃, одновременно снижая риск воздействия пыли во время обработки.
---
II Анализ преимуществ замены антимоната натрия
1. Улучшенная окружающая среда и безопасность
Низкая опасность пыли: антимонат натрия находится в гранулированной или микросфральной структуре, и во время обработки нелегко обрабатывать вдобимую пыль;
Меньше противоречия токсичности: по сравнению с SB2O2 (перечисленным как вещество потенциального беспокойства в результате охвата ЕС), антимонат натрия имеет меньше данных экотоксичности и еще не строго регулируется.
2. Оптимизация производительности обработки
Улучшенная диспергируемость: ионы натрия увеличивают полярность, что облегчает равномерное рассеяние в полимерной матрице;
Сопоставление тепловой стабильности: температура разложения соответствует температуре обработки (200–300 ° C) общих волокон (таких как полиэстер и нейлон), чтобы избежать преждевременного сбоя.
3. Многофункциональная синергия
Функция подавления дыма: Na₂O нейтрализует кислые газы и снижает токсичность дыма (значение LOI может быть увеличено на 2–3%);
Антипада: при сочетании с неорганическими наполнителями (такими как нано-глина), структура углерода становится плотнее.
Iii. Потенциальные проблемы при применении антимоната натрия
1. Баланс между стоимостью и использованием
Высокая стоимость сырья: процесс синтеза антимоната натрия сложна, а цена примерно в 1,2–1,5 раза больше, чем у SB₂O₃;
Низкое эффективное содержание сурьмы: под тем же уровнем огнезащита количество добавления должно быть увеличено на 20-30% (поскольку элемент натрия разбавляет концентрацию сурьмы). Тем не менее, Urbanmines Tech. Ltd., с его уникальными преимуществами исследований и разработок, может оптимизировать стоимость производства антимоната натрия, чтобы они были ниже, чем триоксид сурьмы, и быстро занимать значительную часть доли мирового рынка за полгода.
2. Проблемы технической совместимости
Чувствительность к рН: щелочная Na₂O может влиять на стабильность расплава некоторых смол (например, PET);
Контроль оттенка: остатки натрия при высоких температурах могут вызвать незначительное пожелток волокна, требуя добавления цветовых средств.
3. Долгосрочная надежность должна быть проверена
Разница в сопротивлении погоды: миграция ионов натрия в горячей и влажной среде может повлиять на долговечность огнестойкости;
Проблемы утилизации: процесс химической переработки для натрия, содержащих пламени-снимающиеся волокна, необходимо переработать.
---
IV Рекомендации сценария приложения
Натрий противмонат более подходит для следующих полей:
1. Текстиль с высокой добавленной стоимостью: например, униформа для борьбы с огнем и авиационные интерьеры, которые имеют строгие требования к подавлению дыма и низкой токсичности;
2. Система покрытия на водной основе: пользоваться его диспергируемостью, чтобы заменить подвеску SB₂O₃;
3. Композитная формула огнестойкости: соединена с фосфорс-азот-азотированием, чтобы снизить галогенскую зависимость.
---
V. Будущие направления исследований
1. Наномодификация: повысить эффективность огнестойкости путем контроля размера частиц (<100 нм);
2. Композит носителя на основе био: в сочетании с целлюлозой или хитозаном для развития зеленого пламени-сножившегося волокна;
3. Оценка жизненного цикла (LCA): количественно оценить экологические преимущества всей отраслевой цепочки.
---
Заключение
В качестве потенциального замены триоксида сурьмы, антимонат натрия демонстрирует уникальную ценность с точки зрения экологического дружелюбия и функциональной интеграции, но его стоимость и техническая адаптивность все еще необходимо улучшить. Ожидается, что с более строгими правилами и оптимизацией процесса антимонат натрия станет важным вариантом для следующего поколения огнестойкостей волокна, приводящих в силу отрасль развиваться в направлении высокой эффективности и низкой токсичности.
---
Ключевые слова: антимонат натрия, триоксид сурьмы, огнестойкий, обработка волокна, характеристики подавления дыма
















 IPv6 ПОДДЕРЖИВАЕМАЯ СЕТЬ
IPv6 ПОДДЕРЖИВАЕМАЯ СЕТЬ
